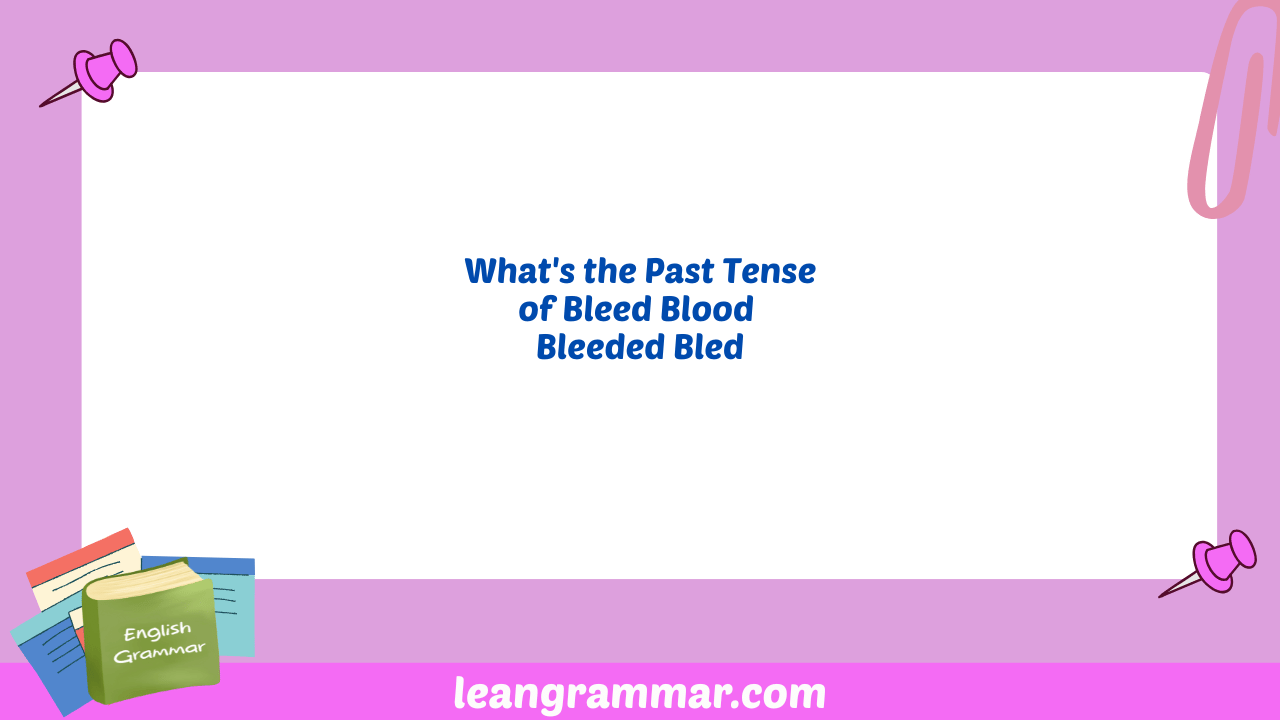
Understanding the correct past tense of irregular verbs like “bleed” is crucial for clear and accurate communication in English. Many learners struggle with irregular verb conjugations, and “bleed” is a common source of confusion.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to the verb “bleed,” its various forms, and its proper usage. Whether you’re an ESL student, a seasoned writer looking for a refresher, or simply curious about English grammar, this guide will help you master the past tense of “bleed” and use it with confidence.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of “Bleed”
- Structural Breakdown: Verb Forms
- Types and Categories of Verb Forms
- Examples of “Bleed” in Different Tenses
- Usage Rules and Guidelines
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Practice Exercises
- Advanced Topics: Figurative Language
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Introduction
Mastering verb tenses is crucial for effective communication in English. Irregular verbs, like “bleed,” often present a challenge because they don’t follow standard conjugation rules.
Using the correct past tense and past participle forms is essential for clarity and grammatical accuracy. This article thoroughly examines the verb “bleed,” covering its definition, various forms, correct usage, and common pitfalls.
This guide caters to learners of all levels, from beginners to advanced English speakers, aiming to solidify their understanding and confidence in using this verb correctly.
This comprehensive exploration of “bleed” aims to equip you with the necessary knowledge and skills to use it accurately in both written and spoken English. We will cover everything from the basic definition to more complex usages, ensuring that you can confidently navigate the nuances of this common yet tricky verb.
By the end of this article, you’ll understand the difference between “bled,” “blood” and the incorrect form “bleeded,” and you’ll be able to use the correct form in various contexts.
Definition of “Bleed”
The verb “bleed” has several related meanings, all revolving around the loss of blood or other fluids. It’s important to understand these meanings in order to use the verb correctly in different contexts.
Let’s explore the core definition and its various applications.
Core Definition
The primary definition of “bleed” is to lose blood from the body. This can be due to an injury, a medical condition, or a deliberate act.
The word describes the act of blood flowing out of a wound or opening.
Expanded Definitions and Contexts
Beyond the literal meaning, “bleed” also has figurative uses. It can describe the leaking of other fluids, such as ink or dye.
Furthermore, it can metaphorically represent the loss of resources, money, or emotional strength. Understanding these extended meanings is crucial for interpreting the verb’s usage in various contexts.
- Literal: To lose blood. Example: He cut his finger and it started to bleed.
- Figurative (Fluids): To leak or seep. Example: The ink from the pen bled through the paper.
- Figurative (Resources): To lose money or resources gradually. Example: The company was bleeding money due to poor management.
- Figurative (Emotions): To feel intense emotional pain or empathy. Example: My heart bleeds for the victims of the tragedy.
Structural Breakdown: Verb Forms
Understanding the different forms of the verb “bleed” is essential for using it correctly in various tenses and grammatical structures. “Bleed” is an irregular verb, which means its past tense and past participle forms do not follow the standard “-ed” ending rule.
Let’s break down the principal parts of the verb.
Principal Parts
The principal parts of a verb are the base form, the past tense, and the past participle. For “bleed,” these are:
- Base Form: bleed
- Past Tense: bled
- Past Participle: bled
Conjugation
Here’s how “bleed” is conjugated in different tenses:
| Tense | Form | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Present Simple | bleed (I/You/We/They), bleeds (He/She/It) | I bleed easily. He bleeds when he shaves. |
| Past Simple | bled | He bled after the accident. |
| Present Continuous | am/is/are bleeding | She is bleeding from the cut. |
| Past Continuous | was/were bleeding | They were bleeding heavily. |
| Present Perfect | have/has bled | He has bled a lot since the injury. |
| Past Perfect | had bled | She had bled before the ambulance arrived. |
| Future Simple | will bleed | He will bleed if he doesn’t get stitches. |
| Future Continuous | will be bleeding | He will be bleeding for a while. |
| Future Perfect | will have bled | By the time they arrive, he will have bled a lot. |
As you can see, the past tense and past participle of “bleed” are both “bled.” This is important to remember to avoid common errors.
Types and Categories of Verb Forms
Understanding the different tenses and how they use the verb “bleed” is crucial for accurate writing and speaking. Let’s explore the main categories of verb forms and how “bleed” fits into each.
Simple Tenses
The simple tenses are the simple present, simple past, and simple future. They express actions that are habitual, completed, or will occur in the future.
- Simple Present: Describes habitual actions or general truths. Example: I often bleed when I cut myself shaving.
- Simple Past: Describes completed actions in the past. Example: He bled profusely after the accident.
- Simple Future: Describes actions that will happen in the future. Example: If you don’t bandage the wound, it will bleed.
Continuous Tenses
The continuous tenses (also known as progressive tenses) describe actions that are ongoing or in progress.
- Present Continuous: Describes actions happening now. Example: She is bleeding from the knee.
- Past Continuous: Describes actions happening in the past over a period of time. Example: He was bleeding all over the carpet.
- Future Continuous: Describes actions that will be in progress at a specific time in the future. Example: He will be bleeding until the doctor arrives.
Perfect Tenses
The perfect tenses describe actions that are completed before a specific time or another action.
- Present Perfect: Describes actions that started in the past and continue to the present, or actions completed at an unspecified time in the past. Example: She has bled a lot since the operation.
- Past Perfect: Describes actions completed before another action in the past. Example: He had bled before the paramedics arrived.
- Future Perfect: Describes actions that will be completed before a specific time in the future. Example: By the time they get there, he will have bled to death.
Examples of “Bleed” in Different Tenses
To solidify your understanding, let’s look at numerous examples of “bleed” used in various tenses and contexts. These examples will help you see how the verb functions in different sentence structures and situations.
Simple Present Tense Examples
The simple present tense is used for habitual actions, general truths, and facts. Here are some examples with “bleed”:
| Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|
| I bleed easily when the weather is dry. | Describes a recurring condition. |
| He bleeds every time he shaves too closely. | Describes a habitual action and its consequence. |
| She bleeds heavily during her periods. | Describes a recurring event. |
| The paper bleeds if you use too much ink. | Describes a general truth about the paper. |
| My heart bleeds for those who suffer. | Expresses empathy as a general feeling. |
| The company bleeds money due to mismanagement. | Describes a continuous loss of resources. |
| He bleeds profusely from even small cuts. | Describes a typical reaction to injury. |
| She bleeds internally sometimes without knowing. | Describes an occasional health issue. |
| The color bleeds when the fabric is washed. | Describes a characteristic of the fabric. |
| The business bleeds cash during the off-season. | Describes a regular financial occurrence. |
| His conscience bleeds when he lies. | Describes a habitual feeling of guilt. |
| The forest bleeds sap from the damaged trees. | Describes a natural process. |
| The radiator bleeds air if it’s not properly sealed. | Describes a functional issue. |
| My gums bleed when I brush too hard. | Describes a common physical reaction. |
| The old pipes bleed rust into the water. | Describes a deterioration process. |
| The team bleeds talent as players retire. | Describes a loss of skilled personnel. |
| The political party bleeds support due to scandals. | Describes a decline in popularity. |
| The painting bleeds color under direct sunlight. | Describes a sensitivity to light. |
| The economy bleeds jobs during recessions. | Describes a cyclical economic event. |
| My soul bleeds when I see injustice. | Expresses a profound emotional reaction. |
| The country bleeds resources to corruption. | Describes a loss due to illegal activity. |
| The narrative bleeds with melancholy in this novel. | Describes the tone of the novel. |
| The battery bleeds charge when it is old. | Describes the characteristic of an old battery. |
| The company bleeds market share due to competition. | Describes a loss of market share. |
Simple Past Tense Examples
The simple past tense describes completed actions in the past. Remember that the past tense of “bleed” is “bled.”
| Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|
| He bled after he fell off his bicycle. | Describes a completed action in the past. |
| She bled all over the new carpet. | Describes the extent of the bleeding. |
| The wound bled for hours before they got to the hospital. | Describes the duration of the bleeding. |
| The company bled money last quarter due to poor sales. | Describes a past financial loss. |
| My heart bled when I heard the news. | Expresses past emotional pain. |
| The ink bled through the old paper. | Describes a past event of ink spreading. |
| He bled profusely from the cut. | Describes the severity of past bleeding. |
| She bled slightly from the scratch. | Describes a minor past injury. |
| The radiator bled air after it was refilled. | Describes the action of releasing air. |
| The color bled when the shirt was washed. | Describes the discoloration of the shirt. |
| His conscience bled after he lied. | Describes the feeling of guilt after lying. |
| The forest bled sap from the damaged trunk. | Describes the release of sap from the tree. |
| My gums bled when I first started flossing. | Describes a past physical reaction. |
| The old pipes bled rust into the water supply. | Describes the contamination of water. |
| The team bled talent as key players retired last year. | Describes the loss of skilled players. |
| The political party bled support following the scandal. | Describes the decline in support. |
| The painting bled color when exposed to the sun. | Describes the effect of sunlight. |
| The economy bled jobs during the last recession. | Describes the job market during recession. |
| My soul bled when I saw the suffering. | Describes a deep emotional experience. |
| The country bled resources due to corruption. | Describes the loss due to corruption. |
| The narrative bled with sadness in the final chapter. | Describes the mood of the chapter. |
| The battery bled its charge overnight. | Describes the loss of battery charge. |
| The company bled market share as competitors emerged. | Describes the loss of market share. |
Future Tense Examples
The future tense describes actions that will happen in the future. Here are some examples using “will bleed.”
| Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|
| If you don’t bandage that cut, it will bleed. | Describes a future consequence. |
| He will bleed if he continues to pick at the scab. | Describes a future result. |
| The company will bleed money if they don’t improve sales. | Describes a predicted financial loss. |
| My heart will bleed if I have to say goodbye. | Expresses future emotional pain. |
| The ink will bleed if the paper gets wet. | Describes a future event of ink spreading. |
| He will bleed more if he doesn’t rest. | Describes the effect of not resting. |
| She will bleed less if she applies pressure. | Describes the effect of pressure. |
| The radiator will bleed air again if it’s not sealed correctly. | Describes a potential future issue. |
| The color will bleed if you wash it in hot water. | Describes how washing affects the color. |
| His conscience will bleed if he chooses the wrong path. | Describes the consequence of a decision. |
| The forest will bleed sap if more trees are damaged. | Describes the consequence of tree damage. |
| My gums will bleed if I skip flossing. | Describes the effect of not flossing. |
| The old pipes will bleed more rust if they’re not replaced. | Describes the consequence of not replacing the pipes. |
| The team will bleed talent as more veterans retire. | Describes the future loss of players. |
| The political party will bleed support if they ignore the voters. | Describes the consequence of ignoring voters. |
| The painting will bleed color if it’s left in direct sunlight. | Describes the effect of sunlight. |
| The economy will bleed more jobs if the recession continues. | Describes the effect of the recession. |
| My soul will bleed if I witness more suffering. | Describes the emotional impact of witnessing suffering. |
| The country will bleed more resources if corruption isn’t stopped. | Describes the consequence of corruption. |
| The narrative will bleed with more emotion as the story unfolds. | Describes the future tone of the narrative. |
| The battery will bleed its charge faster as it ages. | Describes the effect of aging on the battery. |
| The company will bleed market share if it doesn’t innovate. | Describes the impact of not innovating. |
Usage Rules and Guidelines
To use “bleed” correctly, it’s essential to follow specific grammar rules and understand the contexts in which it’s appropriate. Here are the key rules and guidelines.
Correct Tense Usage
Always use “bled” for the past tense and past participle. Avoid using “bleeded,” as it is grammatically incorrect.
Subject-Verb Agreement
Ensure that the verb agrees with the subject in number and person. For example:
- Correct: He bleeds.
- Correct: They bleed.
Contextual Appropriateness
Consider the context when using “bleed” in its figurative sense. Make sure the metaphor is clear and appropriate for the situation.
Active and Passive Voice
“Bleed” can be used in both active and passive voice. However, passive constructions are less common.
- Active: The cut bled profusely.
- Passive: The wound was bled. (Less common, and usually implies a medical procedure)
Common Mistakes to Avoid
One of the most common mistakes is using “bleeded” as the past tense or past participle of “bleed.” This is incorrect; the correct form is “bled.” Here are some examples of common errors and their corrections:
| Incorrect | Correct | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| He bleeded after the accident. | He bled after the accident. | “Bled” is the correct past tense. |
| She has bleeded a lot. | She has bled a lot. | “Bled” is the correct past participle. |
| The wound was bleeded. | The wound bled. / The wound was bleeding. | “Bled” is the correct past participle and “bleeding” is the past continuous. |
| The company is bleeded money. | The company is bleeding money. | “Bleeding” is the correct form for the present continuous tense. |
| My heart bleeded for them. | My heart bled for them. | “Bled” is the correct past tense. |
Another common mistake is misusing the verb in figurative contexts. Ensure that the metaphorical usage aligns with the intended meaning.
Practice Exercises
Test your understanding of “bleed” with these practice exercises. Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verb.
Exercise 1: Simple Past Tense
Complete the following sentences using the correct past tense form of “bleed” (bled).
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. He ________ after he tripped and fell. | bled |
| 2. The cut ________ profusely, staining his shirt. | bled |
| 3. She ________ onto the carpet because of the deep wound. | bled |
| 4. The company ________ money due to poor investments. | bled |
| 5. My heart ________ when I saw the homeless man. | bled |
| 6. The ink ________ through the thin paper. | bled |
| 7. The radiator ________ air until it was properly sealed. | bled |
| 8. The dye ________ from the fabric during the first wash. | bled |
| 9. His conscience ________ after he told the lie. | bled |
| 10. The tree ________ sap from the damaged branch. | bled |
Exercise 2: Present Perfect Tense
Complete the following sentences using the present perfect tense (has/have bled).
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. She ________ a lot since the surgery. | has bled |
| 2. They ________ more than anyone expected. | have bled |
| 3. The organization ________ resources due to corruption. | has bled |
| 4. My heart ________ for the victims of the earthquake. | has bled |
| 5. The ink ________ all over the page because of the humidity. | has bled |
| 6. He ________ from the same wound for days. | has bled |
| 7. The company ________ money consistently this year. | has bled |
| 8. Her conscience ________ every time she makes a mistake. | has bled |
| 9. The pipes ________ rust into the water for years. | have bled |
| 10. The team ________ key players to other teams. | has bled |
Exercise 3: Choose the Correct Form
Choose the correct form of the verb “bleed” in the following sentences.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. He (bleed/bled/bleeded) after he cut himself. | bled |
| 2. She (is bleeding/bleeds/bleeded) heavily from the wound. | is bleeding |
| 3. They (have bled/has bled/have bleeded) a lot of money on this project. | have bled |
| 4. If you don’t stop picking at it, it will (bleed/bled/bleeded). | bleed |
| 5. My heart (bleeds/bled/bleeded) for those in need. | bleeds |
| 6. The ink (bled/bleed/bleeded) through the paper. | bled |
| 7. The company (bled/bleeds/bleeded) money every quarter. | bleeds |
| 8. He (has bled/have bled/has bleeded) from that cut all day. | has bled |
| 9. If he’s not careful, he will (bleed/bled/bleeded) again. | bleed |
| 10. She (was bleeding/bled/bleeded) when I found her. | was bleeding |
Advanced Topics: Figurative Language
The verb “bleed” is often used figuratively to convey a sense of loss, pain, or empathy. Understanding these advanced usages can enrich your understanding of the English language and enhance your writing.
Metaphorical Usage
“Bleed” can be used to describe the loss of resources, money, or energy. For example, “The company is bleeding money” means the company is losing money rapidly.
Emotional Connotation
“Bleed” can also express deep emotional pain or empathy, as in “My heart bleeds for the victims.” This usage conveys a strong sense of compassion and sorrow.
Color Bleeding
In art and design, “bleed” refers to the spreading of ink or color beyond its intended boundaries. This term is commonly used in printing and graphic design.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions about the verb “bleed” and its various forms.
- Is “bleeded” a correct form of the verb “bleed”?
No, “bleeded” is not a correct form. The past tense and past participle of “bleed” are both “bled.”
- When should I use “bled” instead of “bleed”?
Use “bled” when referring to a completed action in the past or as the past participle in perfect tenses (e.g., “He bled after the fall,” “He has bled a lot”).
- Can “bleed” be used in the continuous tense?
Yes, “bleed” can be used in the continuous tense (e.g., “He is bleeding,” “He was bleeding”).
- What does it mean when someone says, “My heart bleeds for you”?
It means they feel deep sympathy or sorrow for you. It’s an expression of strong empathy.
- How is “bleed” used in business contexts?
In business, “bleed” often refers to the loss of money or resources (e.g., “The company is bleeding money”).
- What is the past participle of “bleed”?
The past participle of “bleed” is “bled.”
- How can I remember that the past tense of “bleed” is “bled”?
Associate “bleed” with other irregular verbs that change their vowel in the past tense, such as “feed” (fed), “lead” (led), and “read” (read – pronounced red).
- Is it correct to say “The wound was bled”?
While grammatically possible, it is uncommon. It’s more common to say “The wound bled” or “The wound was bleeding.” “The wound was bled” might be used in a medical context to describe the action of a doctor or nurse draining blood, but this usage is rare.
- What does color bleeding mean in the context of art?
Color bleeding refers to the unwanted spreading of one color into another. This can occur in painting, dyeing, or printing, resulting in blurred or indistinct edges.
- Can “bleed” be used in the passive voice?
Yes, but it’s not as common as the active voice. For example: “The radiator needs to be bled” (meaning the air needs to be released). However, active voice is usually preferred: “You need to bleed the radiator.”
- What’s the difference between “bleed” and “hemorrhage”?
“Bleed” is a general term for losing blood. “Hemorrhage” refers to a profuse or rapid loss of blood, often due to a severe injury or medical condition. Hemorrhage is a more serious and specific term.
Conclusion
Mastering the verb “bleed” and its various forms is essential for clear and accurate communication in English. Understanding the difference between “bleed” and “bled,” avoiding the common mistake of using “bleeded,” and recognizing the verb’s figurative usages will significantly improve your writing and speaking skills.
By following the rules and guidelines outlined in this article, you can confidently use “bleed” in a variety of contexts.
Remember to practice using “bleed” in different tenses and contexts to reinforce your understanding. Pay attention to the subject-verb agreement and the appropriateness of the verb in figurative expressions.
With consistent practice and attention to detail, you’ll master the nuances of this verb and use it with accuracy and confidence. Keep practicing and exploring the English language, and you’ll continue to improve your grammar skills.